Introduction
In this final post of the series on the Ray framework, we will delve into the use of its RLlib (Reinforcement Learning Library) to train reinforcement learning algorithms in simulated and real environments, and how to use the full power of Ray to train, tune, and serve them.
Ray is a Python framework that allows for the parallel and distributed execution of Python applications. It is primarily designed for use in Machine Learning and AI applications, but it can also be used in any Python application that requires distributed computing.
In the first post of the series, Ray Cluster, we saw how to deploy a Ray cluster on a single machine with Docker (Docker Compose) and briefly explained the different parts of the framework: Ray Data, Ray Train, Ray Tune, Ray Serve, and how the latter, Ray Serve, can be used to serve a Hugging Face model that translates texts from English to French.
And in the next one, Ray Cluster II, we deployed an on-premise Ray cluster on several production machines and how to train and serve the machine learning models our products need on it.
RLlib Reinforcement Learning with Ray
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an area of machine learning (ML) inspired by the trial-and-error learning used by humans, where an Agent learns to make optimal decisions in an environment to maximize a cumulative reward. Unlike supervised learning, where the Agent is provided with a dataset of inputs and outputs, in RL, the Agent learns on its own through interaction with the environment.
Key components of reinforcement learning:
- Agent: The entity that makes decisions and interacts with the environment.
- Environment: The world in which the Agent operates, providing the Agent with state information and rewards for its actions.
- Actions: The options available to the Agent in each state.
- State: The representation of relevant information from the environment for the Agent at a given time.
- Reward: The feedback signal that tells the Agent how good its action was.
- Value Function: Estimates the expected long-term reward from a given state.
- Policy: Defines the probability of the Agent taking each action in each state.
How a reinforcement learning algorithm training works:
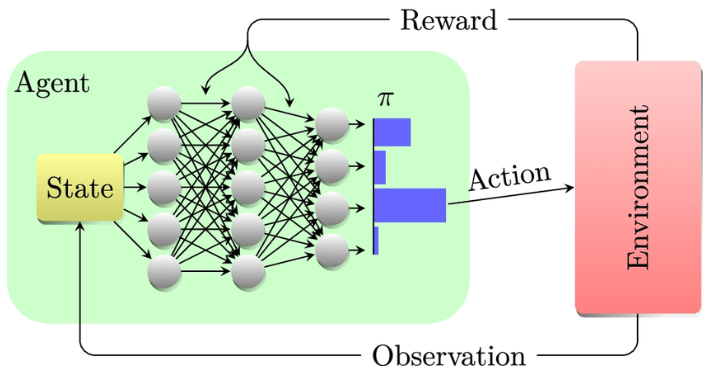
- 1.- The Agent observes the current state of the environment.
- 2.- It selects an action according to its current policy (which it will refine during training).
- 3.- The environment executes the action and provides the Agent with a new state and a reward.
- 4.- The Agent updates its value function and its policy based on the reward received.
- 5.- Steps 1-4 are repeated until the Agent reaches a terminal state or a stopping criterion is met.
When the training ends, the Agent is able to “move” through the environment and, depending on its state, decide which action to take to solve the problem (maximize the cumulative reward).
Ray RLlib is a scalable and distributed reinforcement learning library that provides a high-level implementation of reinforcement learning algorithms.
RLlib integrates with Ray to provide a simple and scalable API for training and evaluating reinforcement learning models. RLlib includes implementations of state-of-the-art reinforcement learning algorithms and tools for evaluating and analyzing the results of those learning trainings.
RLlib Usage Examples
Frozen Lake
The Frozen Lake problem is a classic reinforcement learning (RL) environment. This environment simulates a scenario where an Agent must navigate a frozen lake to reach a goal. The lake is made up of tiles, some of which are safe and others are holes in the ice. The Agent can move in the four cardinal directions (up, down, left, and right). If the Agent moves to a tile with an ice hole, it falls in and receives a negative reward. The Agent’s goal is to reach the target tile in the fewest possible steps, avoiding falling into the ice holes.
In RLlib’s reinforcement learning algorithms, you can use environments defined with the Gymnasium library from OpenAI.
In Gymnasium, you can find many predefined reinforcement learning environments, such as Frozen Lake, which can be used to train reinforcement learning Agents.
Let’s redefine the Frozen Lake environment from Gymnasium to understand the concepts of reinforcement learning and train an Agent with RLlib.


